Book an Ultrasound Scan
To book an Ultrasound Scan Call us Now at 1800 120 51600
Learn MoreFetal medicine, also known as maternal-fetal medicine (MFM) is a subspecialty of obstetrics that focuses on the health of the mother and fetus before, during, and after pregnancy. Fetal medicine has advanced in many ways to monitor and manage maternal and fetal health, including through technological innovations and medical breakthroughs.
Fetal Medicine Specialists are obstetricians and gynaecologists with additional training in managing high-risk pregnancies. They work with pregnant women and their primary obstetricians to address complications and optimize the health of both the mother and the fetus. Petals Imaging offers one of the best Fetal medicine Services in Kolkata. Learn why?
Role of Fetal Medicine in Obstetrics
Fetal medicine represents a significant advancement in the way pregnancies are monitored and managed compared to traditional or "old-school" pregnancy care. Traditional care relied on physical assessments, such as measuring the belly (fundal height) to estimate fetal growth, using a stethoscope to hear the baby’s heartbeat, and monitoring maternal symptoms. Ultrasound was used sparingly and mainly for basic imaging. Fetal medicine combines cutting-edge technology, advanced imaging, and specialized knowledge to provide a much deeper understanding of fetal and maternal health.
Here’s are some of the key differences between getting Pregnancy Monitoring done at a Fetal medicine Clinic vs a non-specialised Ultrasound clinic. 1. Advanced Diagnostics Old methods used physical measurements and basic ultrasounds. Fetal medicine employs cutting-edge tools like 3D/4D ultrasounds, Doppler imaging, and fetal MRIs to provide detailed insights into fetal health. 2. Fetal-Centric Approach Traditional care focused on maternal health as a proxy for fetal well-being. Fetal medicine treats the baby as an individual patient, conducting specialized tests to monitor development. 3. Early Detection Old-school care often identified abnormalities late, sometimes after birth. Fetal medicine detects issues like heart defects or growth restrictions early, enabling timely interventions. 4. Specialized Interventions In the past, care was limited to post-birth treatments. Fetal medicine offers in-utero procedures, such as blood transfusions and surgeries, to address complications during pregnancy. 5. Tailored Risk Management Traditional care took a generalized approach. Fetal medicine customizes care based on high-risk factors like advanced maternal age, multiple pregnancies, or preexisting conditions. 6. Multidisciplinary Collaboration Old-school monitoring involved fewer specialists. Fetal medicine centers integrate obstetricians, neonatologists, and genetic counselors for comprehensive care. 7. Evidence-Based Decisions Fetal medicine uses advanced data from imaging and tests to guide care, while old methods relied more on experience and symptoms. By prioritizing precision, early detection, and tailored interventions, fetal medicine ensures the best outcomes for both mother and baby, far surpassing the capabilities of traditional pregnancy monitoring.Here’s a list of typical scans performed during pregnancy, arranged chronologically by weeks:
Important screenings done in conjunction with maternal-fetal medicine include:
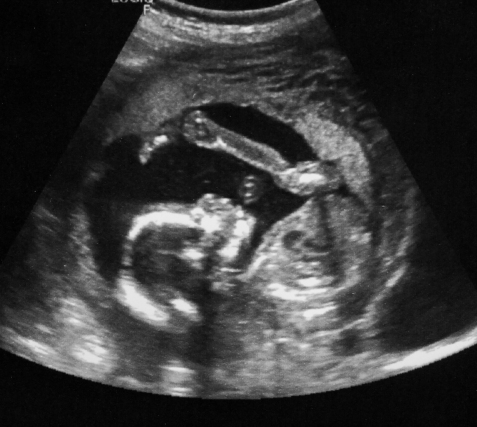
Used to assess the overall health and development of the fetus, including growth, position, and amniotic fluid levels.
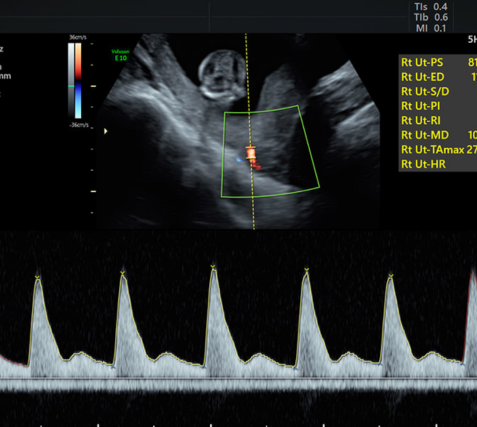
Tests that evaluate the risk of genetic disorders in the fetus without needing invasive procedures via blood tests and an ultrasound scan at specified weeks of Gestation.

Fetal Diagnostic procedures, including Chorionic Villi Sampling, Amniocentesis and Fetal Intervetions like Fetal reduction. Only Certified Genetic Clinics – Ultrasound Clinics with Genetic Diagnosis licences from the government are allowed to do these procedures. These procedures are done by skilled and experienced Fetal Medicine specialists only, as these procedures are slightly invasive and have a slight risk. They are only done as a confirmatory test when primary screening tests show a strong indication of risks to the fetus and pregnancy outcome. Sometimes, Fetal Intervention can be carried out to correct the risks.
Aesthetic procedures aim to enhance one’s physical appearance, boost self-confidence, and promote a sense of well-being.
Maternal Fetal Medicine (MFM) is a specialized branch of obstetrics focused on managing complex pregnancies and ensuring the health of both the mother and fetus. This field uses a range of advanced diagnostic tools and scans to monitor fetal development, detect abnormalities, and assess maternal well-being throughout pregnancy. Key scans in MFM include NT scans, second-trimester anomaly scans, fetal viability and wellbeing scans, Doppler studies, and specialized imaging like fetal echocardiography and neurosonograms. Together, these scans provide a comprehensive understanding of fetal health, enabling early detection and management of potential complications for better pregnancy outcomes.
Ultimately, regular and timely scans lead to improved pregnancy outcomes by allowing for early diagnosis, timely treatment, and well-planned care, ensuring the best possible health for both mother and baby.
If you are pregnant and looking for a reliable and trustworthy ultrasound centre, book your pregnancy scans at Petals Imaging. We are operational at three locations across Kolkata. Here’s why your scan experience at Petals Imaging will be the best in Kolkata:
Yes fetal medicine provides maternal and fetal care during and after the pregnancy.
A clinic with a team of fetal medicine specilaists and inhouse ultrasound facilioties are best equipped to handle High-Risk Pregnancies. As women with these pregnancies need more frequent monitoing and specilaised monitiring under fetal medicine experts. At Petals Health our obstetric team and fetal medicine experts who deliver exceptional care for high-risk moms throughout pregnancy and afterwards. Our clinics also have experienced Pediatric Specialists to care for your baby needs post delivery.
Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome occurs by intrauterine blood transfusion from one twin (donor) to another twin (recipient). It only occurs in monozygotic (identical) twins with a monochromic placenta.
An opne fetal surgery is done to keep the detected abnormalities from becoming life-threatening.
We have expert doctors to diagnosis the fetal conditions precisely, fetal therapy is started at any point during the pregnancy. The experts provide the treatment plan based on the condition.
Yes, at Petals Imaging maternal-fetal care includes prenatal counseling and postnatal care for you and your child.
Petals Imaging - Fetal medicine department offers service like transvaginal scans, and pre-term labour screening.